Repeating code over and over again known as a loop. And is
also a fairly common scenario in programming. Python provide couple of ways to
doing that.
Why we use loop in programming?
There may be some situation where we need to execute a block
of code again and again or we want to execute some lines of code repeatedly. A loop
in programming languages allows us to execute a statement or block of statement
multiple times.
Like other programming languages, python provide following
types of loops to handle such type of scenario where we need to execute code or
block of code repeatedly.
- While Loop
- For Loop
While Loop
To repeat some lines of code or block of code while a given
condition is TRUE. In while loop the controls goes to loop body after testing
some condition.
Example:
def main():
x = 0
# define while loop
while(x < 5):
print("value of x: ",x)
x = x +1
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Code Description:
The above code snippet is a while loop and the content of
while loop is indented that indicates that these line of code belong to the
while loop and not to the main part of the function. So while loop executes
while the condition contain inside the parenthesis is TRUE. So guys while the
condition x is less than five we are
going to print the value of x inside the while loop, and also we are going to
increment the value of x by one (1). Other programming languages like C, C++,
C# etc provide a bunch of ways to do these simple kinds of things using (while,
do while loops etc). Python likes to keep things simple. In python there are
two ways to doing this while and for loop.
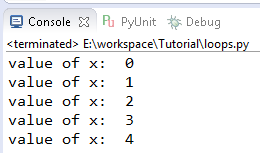
Output
In initial state the value of x is 0 so the output of the
above code starts with 0 and prints the value until the condition in parenthesis
no longer TRUE. So the output is 0,1,2,3,4 and so the loop terminate.
For Loop
For loop in python is little bit different like other programming
languages (JavaScript, C++ and Java). These types of language have the concept of
index variable that counts the number of iteration in for loop.
So for example in JavaScript the syntax of for loop is looks
like this.
for (i=0,i<10,i++){
// your logic goes here
}
In above code a
counter variable i=0 is used to control the execution of the loop. That’s not
is used in python to operate the loops in python. Python for loops are called iterator.
So in this case if I want have x to loop
over the range of numbers than I need to use python built in range() function.
So I have a range going to 4 to 10 in for loop and inside the loop I have a
print statement that will prints the value of x.
#!/usr/bin/python3
def main():
x = 0
# define a for loop
for x in range(4,10):
print("Value of x: ",x)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
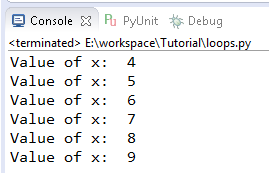
Output
In output window you can see that its printed out 4 to 9 so x within the range which is not obviously is not inclusive of 10. So it exclude the number 10 right here. That’s why it printed out the number 4 to 9. For loops not
only operates on number it also operates on sets of things such as collections,
objects and lists. Here collections mean a set of or a list of objects for
example a list of or a collection of day's name.
Object of data comes from database
For example we have a database of a university and in that
database we have a table named "tbl_student" and in that table we
have 3 records. So the object looks like "tbl_student(1,2,3)". So
here we operates or execute our for loop in "tbl_student" instead of
number or range of numbers.
Data comes from Collections/List
For example a list of day's, list of months and list of data
which we need to loop through.
Days = ["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"]
Use a for loop over a collection/list
#!/usr/bin/python3
def main():
# use a for loop over a collection/list
list_of_days = ["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"]
for day in list_of_days:
print("Day Name: ",day)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Code Description
In the above code I declared a variable name list_of_days
and I am initializing this to a list of days using opening and closing square
bracket. And inside of the bracket I have my day name. Now I am going to loop
through the list and printing out the day. Here we are not using any number
instead we are iterating the for loop for each member of the list item. And the
print statement will prints out the day name.
So its looping over the content of the list item, again here no indexed counter involved just iterating over the member of a list.
Loop control statements
Python loop control statement will change the execution of a
loop. For example on some condition we want to stop or continue the loop
iteration. In python we have "break" and "continue" key
word to stop/break or continue the loop execution.
Break statement
The break statement is used to break the execution of a loop
if a condition is met.
#!/usr/bin/python3
def main():
# use of break loop control statement
for x in range(5,10):
if x == 7: break
print("x: ",x)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
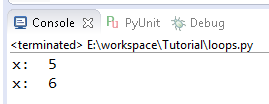
In above code If x is equal to 7 than break, the break
statement is here will cause to terminate the for loop and fall through the
next block of code. When we run this program this will print out only 5 and 6
because when the condition is met the break statement will kicks out the loop.
Continue statement
The continue statement skips the rest of the statement when
it is encounter.
#!/usr/bin/python3
def main():
# use of continue loop control statement
for x in range(5,10):
if (x % 2 == 0): continue
print("x: ",x)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
In above code our condition is if x modulus 2 is equal to 0
or in other word take x and divide it by 0 if the value left over is 0 than
continue. Its mean if the condition is met don't go to the next line (in our
case the next line is print statement) just go back up to the start of the
loop. In simple word if I come across in the even number doesn't print out that
number. The continue statement will skip the next line if the condition will
met. This will print out 5,6 and 9.





0 Comments