Now that we have learned basics of python language, we are
going to turn our attention to using the rich library of predefined code that
comes with python In order to build functionality in python application. In
this tutorial we focus on manipulating dates and time in python programming.
In order to get this rich functionality that python provide
into your applications you have to tell the python interpreter to go to and get
it somewhere. And the way you doing that is something call "import"
statement.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from datetime import date
from datetime import time
from datetime import datetime
What I am doing here is telling the python interpreter that
from the "datetime" module I want to import date,time and datetime
classes. These are predefined pieces of functionality in the python library
that let me manipulates date and times. So I don’t have to write this code it's
already written for me in the shape of library/classes. To use this
functionality I just need to import it.
Now that we have imported date object so let's start working
on dates.
def main():
# Date Object
# get todays date from the today() method from the built-in python date class
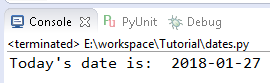
today = date.today()
print("Today's date is: ",today)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
In above code I am declaring a variable named
"today" and I am saying today equal date.today() that will give me
today's date and in next line I am simply printing whatever I got.
Output
Here "today" is an object that comes from build-in
python library "date.today()" function. So today object has several
properties associated with it. So I can get the individual day, individual
month and year from that today object.
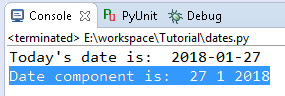
#print out the date individual components
print("Date component is: ",today.day, today.month, today.year)
Output
We got individual date component such as day, month and
year. So now I can work with these individual components whenever I want to do
date manipulations.
The date object also provides some useful properties that I can
use in some other advance feature of my applications. For example I can
retrieve weekday number. That starts from (0=Mondy) to (6=Sunday). So I had
some list that I want to providing index variable that depend on weekday I can
use the weekday property to indexing to a list of say abbreviated day name or
something else that represent a collection of days. So that just return an
integer number.
Output
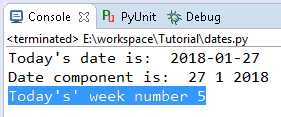
You can see that today's weekday number is 5, so today is
Saturday. Below is complete example of Date object.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from datetime import date
from datetime import time
from datetime import datetime
def main():
# Date Object
# get todays date from the today() method from the built-in python date class
today = date.today()
print("Today's date is: ",today)
#print out the date individual components
print("Date component is: ",today.day, today.month, today.year)
#retrive todays weekday (0=Mondy, 6=Sunday)
print("Today's' week number",today.weekday())
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Now let's start with datetime object. So just like working
with dates I can get time as well.
So using the datetime class instead of date class I am
calling the "now" functions. That would give me the current date as
well as time.
def main():
# Datetime Object
# get todays date from the datetime class
today = datetime.now()
print("The current date and time is: ",today)
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Output
You can see that the output shows current date and time. In
time you got hours, minuets, second and milliseconds.
Now let's just get the time. To get the current time we need
to get the time portion of the datetime object. So I declared a variable
current_time and I am going to construct a time object given a full date and
time as an argument from a datetime class. This will give me just the time. So
the output shows just the time.
#Get the current time
current_time = datetime.time(datetime.now())
print("The Current Time is: ",current_time)
Output
Remember weekday operator gives me the numbers from 0 to 6
depending what the current weekday is. So to get name from the given numbers I am
declaring the week name (Monday to Sunday) array or list. What I am going to do
is get the weekday and print that out and again printing out the list indexed
by the weekday number.
# weekday returns number 0 to 6 means (Monday to Sunday)
wd = date.weekday(today)
days = ["Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday","Sunday"]
print("Today is day number: ",wd)
print("The Day is: ",days[wd])
Output
You can see the today is day number 5 and the day name is
Saturday. So in the above code I get the today and pass that day to the
built-in python function weekday to get number of that day. After getting it we
pass that number as an index to our created list named "days". That
will give us the name of that day. Below is given the complete code.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from datetime import date
from datetime import time
from datetime import datetime
def main():
# Datetime Object
# get todays date from the datetime class
today = datetime.now()
print("The current date and time is: ",today)
#Get the current time
current_time = datetime.time(datetime.now())
print("The Current Time is: ",current_time)
# weekday returns number 0 to 6 means (Monday to Sunday)
wd = date.weekday(today)
days = ["Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday","Sunday"]
print("Today is day number: ",wd)
print("The Day is: ",days[wd])
if __name__ == "__main__": main()
That’s the quick introduction of dates and time in python programming language.







0 Comments